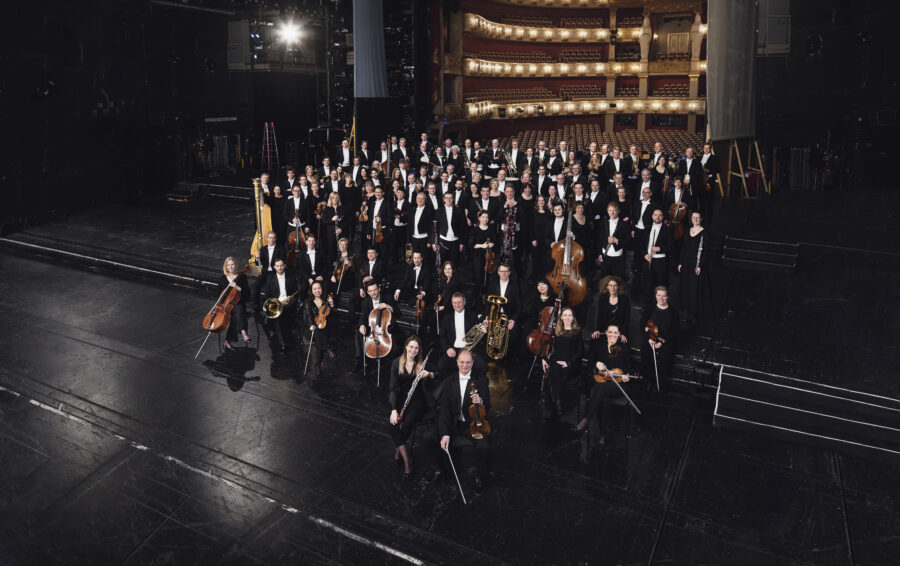
History looms large when you’re 500 years old. The Bayerisches Staatsorchester might know a thing or two about the weight of such a history – but in-house record label Bayerische Staatsoper Recordings renders the present, as much as the present and future, profound, polished, and yes, portable.
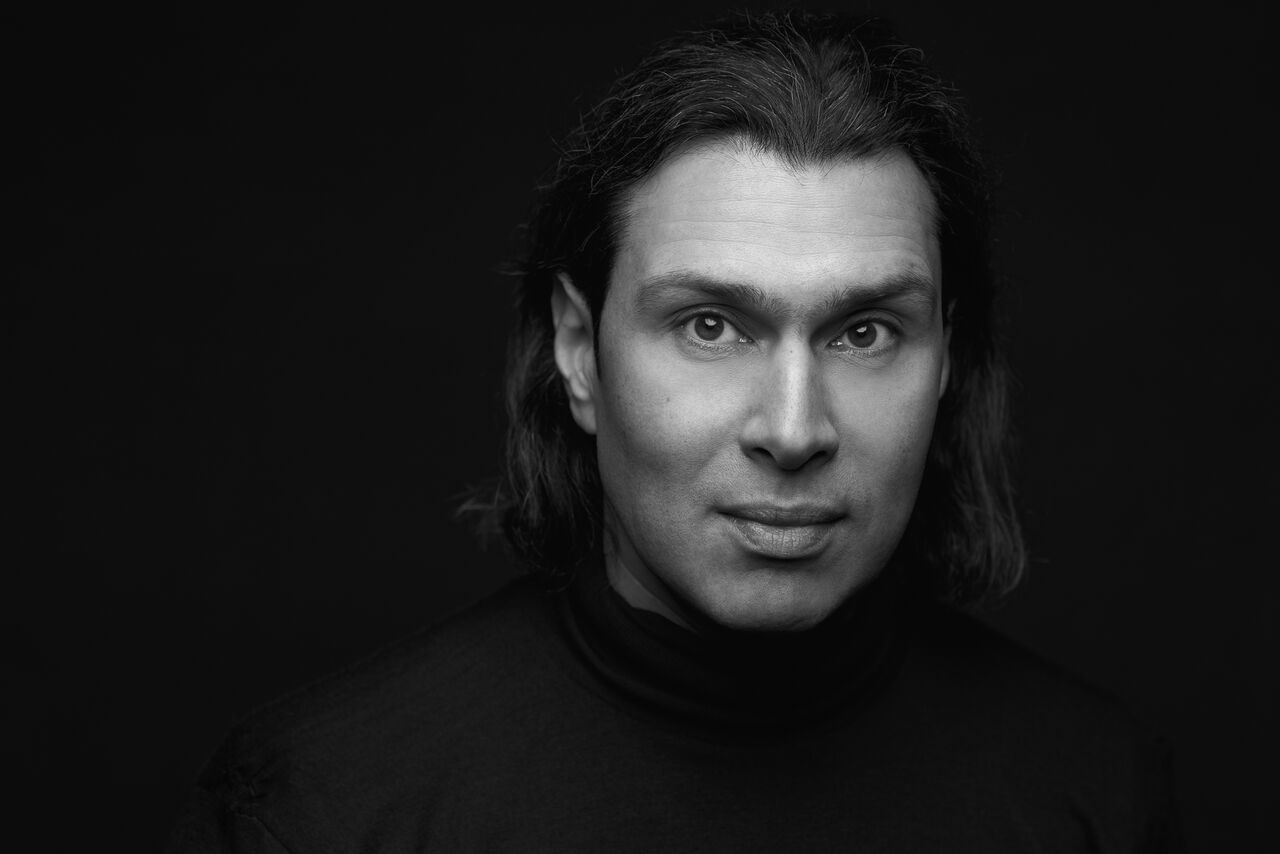
The orchestra of the famed Bayerische Staatsoper began life in 1523, when regularized performances started at the Bavarian court. Its musicians became famous following the 1563 appointment of composer Orlande de Lassus, though their output was reoriented with the start of opera performances in the mid 17th century in Munich. Mozart himself led the orchestra in the world premiere of Idomeneo in 1781, which was also written in the city. But it was 1811 when, crucially, members of the Bavarian court orchestra found the Musikalische Akademie e. V. association; that decision led to the creation of Munich’s first public concert series, known as Akademiekonzerte. The orchestra gained particular fame in the latter half of the 19th century in their hosting the first performances of numerous Wagner operas, including Tristan und Isolde (premiered at the National Theatre in 1865) Die Meistersinger von Nürnberg (1868), Das Rheingold (1869), and Die Walküre (1870). One of the institution’s most famous General Music Directors (GMDs) was composer Richard Strauss, whose father Franz was a noted principal horn player with the orchestra, then known as the Court Opera. But Strauss Jr. was far from the only famous music figure in the position; subsequent leaders have included a who’s who in classical history, including Bruno Walter, Clemens Krauss, Georg Solti, and more recently, Zubin Mehta, Kirill Petrenko, and currently Vladimir Jurowski, who led acclaimed productions of Prokofiev’s War and Peace and Brett Dean’s Hamlet last season. Whether either will see their way to formal releases remains to be seen.

BSOrec CD releases. Photo: mine; please contact me to reuse.
Bayerische Staatsoper Recordings (or BSOrec), run in-house, will be the label to make it happen. The independent announced itself in 2021 in a rather unique fashion, not with a splashy opera production but via big symphony – Mahler’s immense Seventh Symphony, to be precise. Captured live in 2018 and led by contemporaneous GMD Petrenko, the recording – and indeed label – generated big buzz across the classical world, with many music writers noting the orchestra’s responsiveness to the material. In a review for Gramophone at its release in 2021, Edward Seckerson wrote that “I really thought I knew this work – every facet of it. But Kirill Petrenko has a way of hearing deep into textures and harmonies that is at times really quite startling. He gives us X-ray ears.” The label quickly followed the Mahler release with a DVD of the acclaimed 2019 staging of Korngold’s Die Tote Stadt featuring tenor Jonas Kaufmann and soprano Marlis Petersen. In his assessment at Adventures In Music, classical blogger Jari Kallio praised Video Director Myriam Hoyer while noting that “the orchestral lines are drawn with acute intensity and tremendous sonic beauty.” In early 2022 the label released a DVD of The Snow Queen by composer Hans Abrahamsen and conducted by Cornelius Meister. Based on a fairytale by Hans Christian Andersen, the presentation features Barbara Hannigan and was recorded in late 2019-early 2020. All three releases went on to achieve significant accolades within the classical world, including four big wins at the 2022 Gramophone Awards. It was the first time in the history of the prestigious British organization that a Recording of the Year was won by an audio-visual title; it was also only the second time an orchestra won both the Orchestral and Opera categories. Quite the achievement for a young label.

BSOrec DVD releases. Photo: mine; please contact me to reuse.
BSOrec marched on, releasing DVDs of a combined ensemble production of Stravinsky’s Mavra and Tchaikovsky’s Iolanta (released in 2022) and Andrea Chénier (released last month) again featuring Jonas Kaufmann and led by Marco Armiliato. It’s a curious if inspired selection, with an even more curious choice of design; in place of cover photos is bold silver lettering, with not one name larger than the other, set within sturdy holders, each in solid, rainbow-like colours. The eye-catching design, originally by Mirko Borsch, sends a clear message across both audio and video titles, along with the many thoughtful essays and interviews contained within, the majority penned by talented dramaturg Malte Krasting, who knows a thing or two about the role of context.
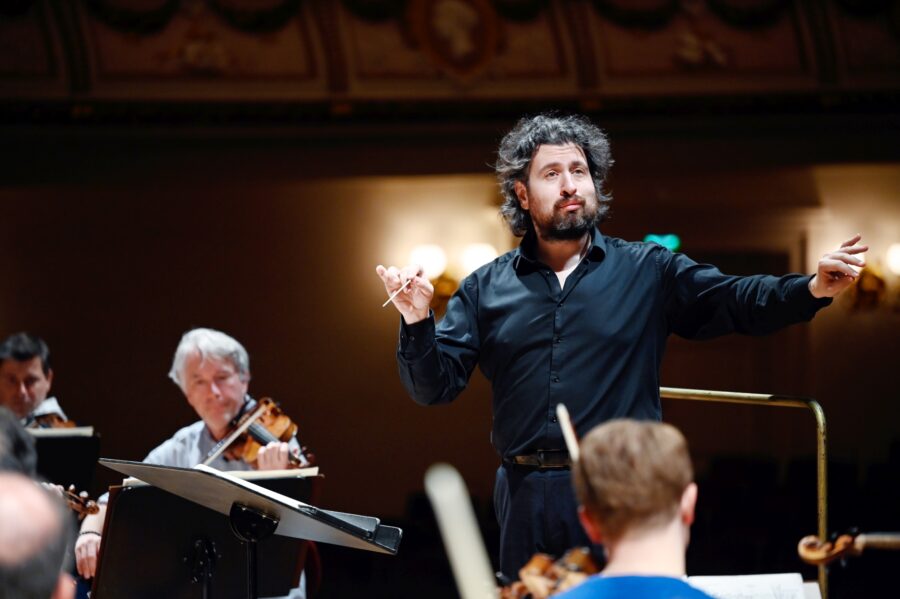
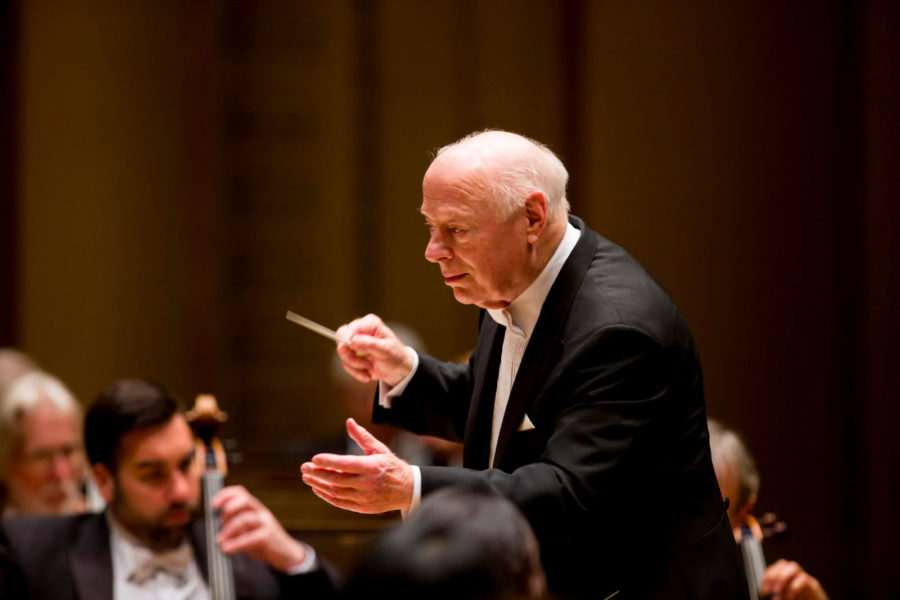
The first BSOrec release with current General Music Director Jurowski (from 2022) pairs Brett Dean’s Testament and Beethoven’s Second Symphony, and includes Krasting’s thoughtful interview with the Russian maestro in its liner notes. Releases (all of which enjoy distribution via Naxos) this year have marked the 500th birthday of the Bayerisches Staatsorchester though they also highlight the unique talents of individual sections. Original Grooves by Opercussion, and Voyager by the Munich Opera Horns, both released earlier this year, are a showcase of creative thinking within the recording paradigm. Original Grooves features a creative mix of classical, Latin, and jazz (Bach, Astor Piazzolla, Dizzy Gillespie) in original arrangements by ensemble members. Voyager offers music by Strauss, Dubois, Reicha, and Franz alongside compositions by contemporary composers Urs Vierlinger, Hans-Jürg Sommer, and Konstantia Gourzi. Such interlacing of sounds, with a keen eye on drama, was also realized via the the release of contemporary children’s piece Der Mondbär: Ein Hörspiel mit Musik für Kinder, with music by Richard Whilds/ libretto by Sarah Scherer, and based on the popular German books and animated series. BSOrec’s upcoming audio release is a firm nod to its storied history, if also an ambitious wave to the future. Mendelssohn’s Elias was captured in July 1984 and features a dream team of soloists (Dame Margaret Price, Brigitte Fassbaender, Peter Schreier, Dieter Fischer-Diskau) and choir (Chor des Städtischen Musikvereins zu Düsseldorf), led by celebrated conductor (and former company leader) Wolfgang Sawallisch.

Conductor and former Bayerische Staatsoper GMD Kent Nagano meets with Bayerisches Staatsorchester in Hamburg September 10, 2023. Photo: Geoffroy Shied
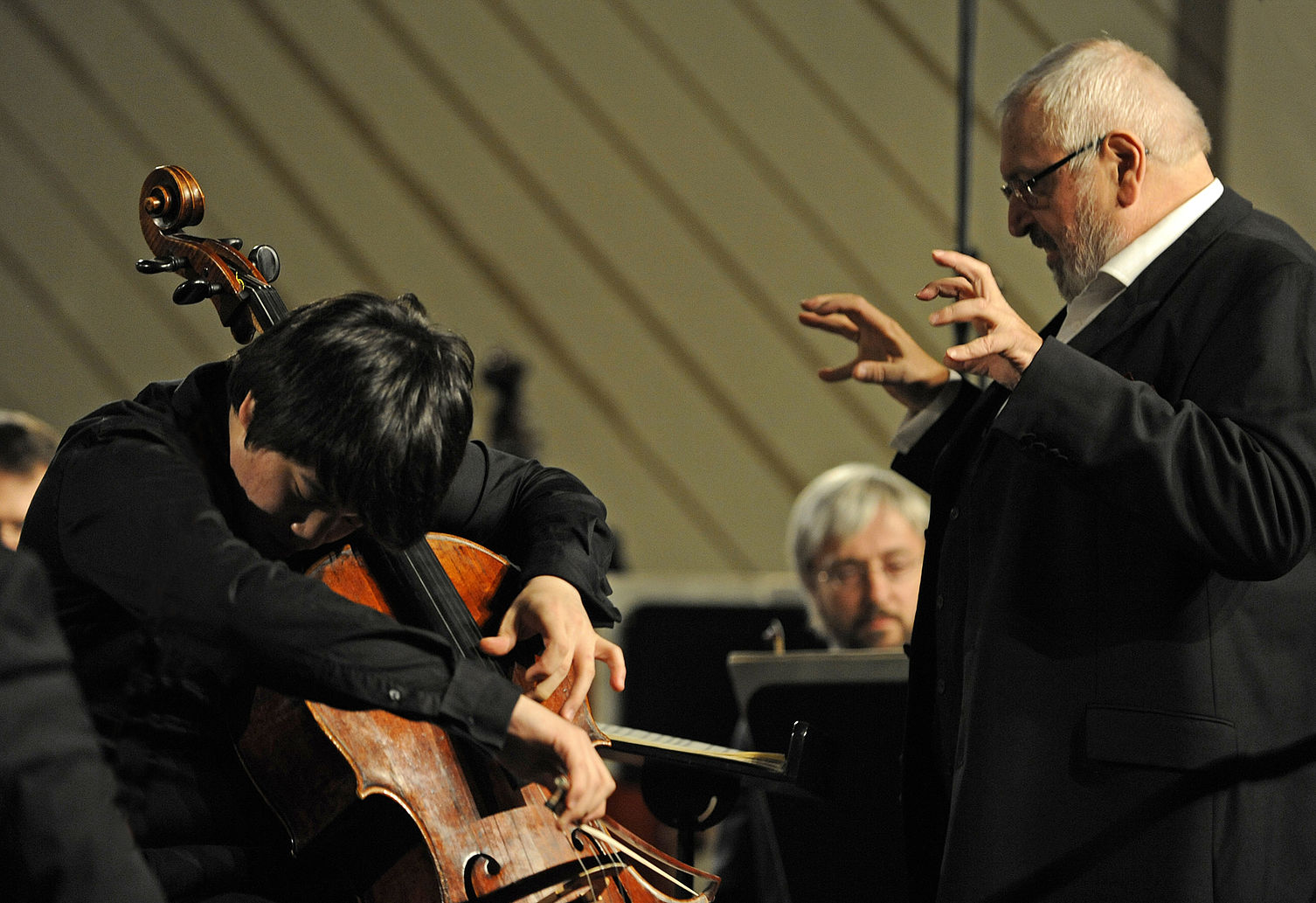
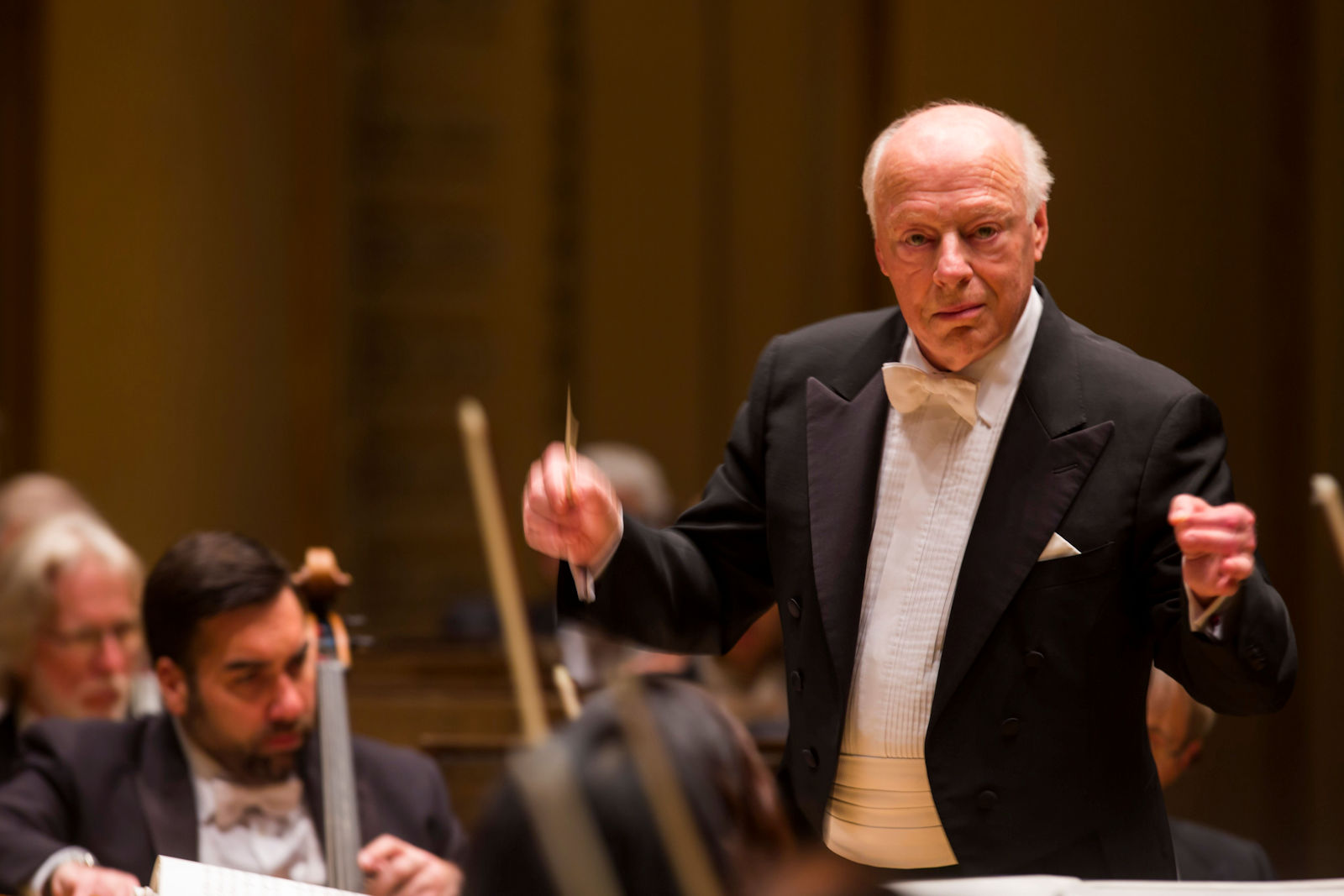
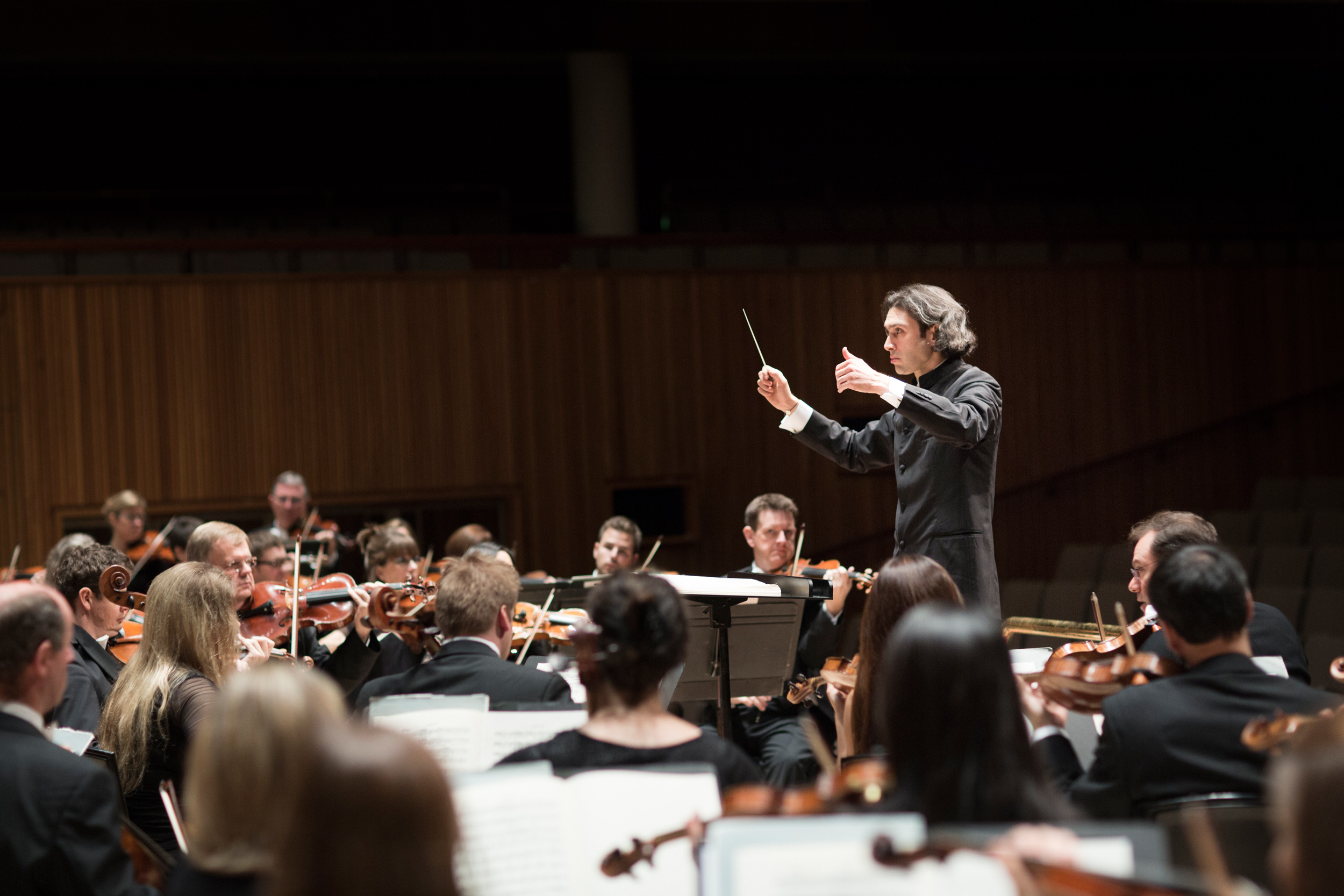
Such an auspicious combination of elements (past/present; theatricality; dramaturgy; passion) could be experienced through recent concerts given as part of the orchestra’s recent European tour, which included stops in London, Paris, and Berlin. Tour repertoire was chosen thoughtfully, a true reflection of not only composer connections to Bayerische Staatsoper (Wagner, Strauss) but to the orchestra’s home city as well (Mahler’s Fourth Symphony was premiered in Munich in late 1901). Past and present mixed in certain programmes, with Ukrainian composer Victoria Vita Poleva’s Symphonie Nr.3 White Internment opening select concerts, and soloists ran the gamut between generations, with violinist Vilde Frang, pianist Yefim Bronfman, and sopranos Louise Alder and Elsa Dreisig. The orchestra’s stop in Hamburg included a visit with conductor and former GMD Kent Nagano; on their home turf in Munich they entertained over 10,000 spectators who had gathered in Marstallplatz as part of an “Oper für Alle” event which featured the music of Schumann and Strauss. Earlier in the month in Lucerne, the orchestra’s performance of Bruckner’s Fourth Symphony was interrupted by climate activists whose presence was acknowledged with utmost diplomacy by conductor Jurowski; it was a moment of elegant humanism, a quality deep within the orchestra’s DNA and palpable throughout BSOrec’s output, and its small if highly dedicated team, led by Managing Director Guido Gärtner.

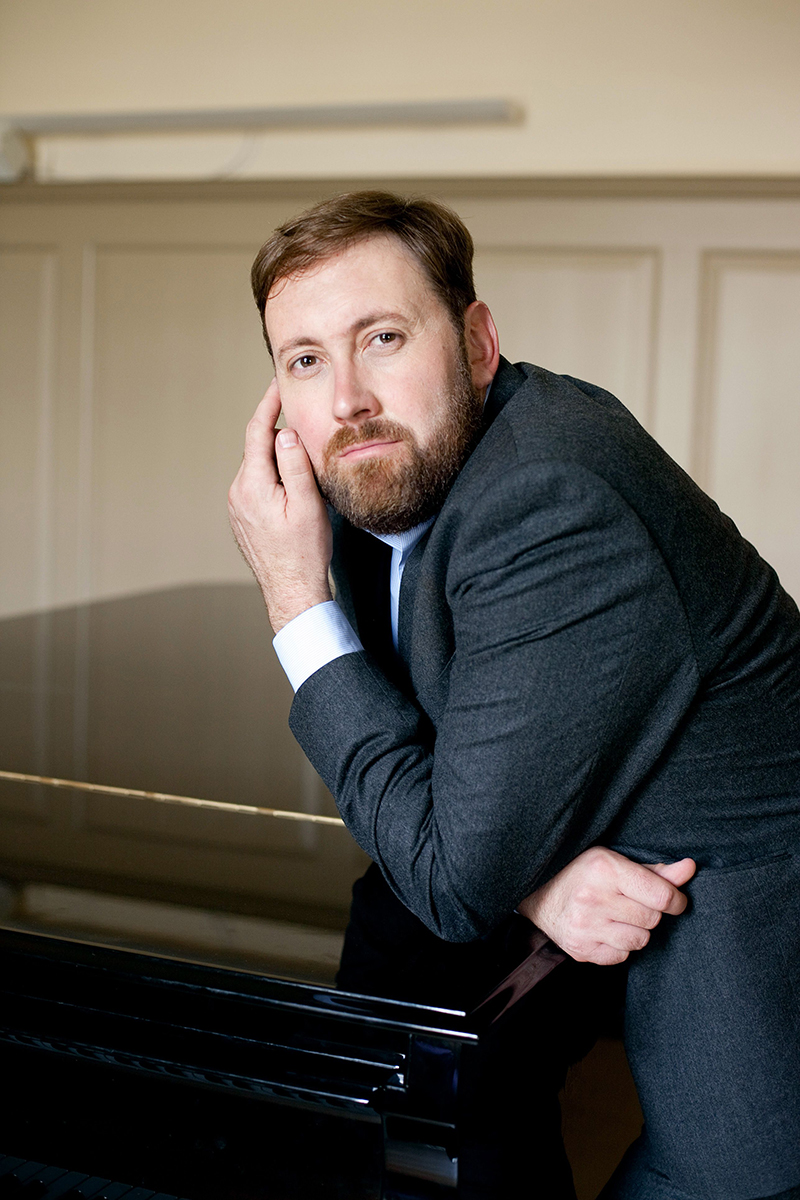
BSOrec’s Guido Gärtner. Photo: Frank Hanewacker
Gärtner joined the Bayerisches Staatsorchester in 2008 as a violinist, a position he continues concurrent to BSOrec duties. He and I enjoyed a wide-ranging conversation in late summer, which touched on a myriad of topics, including that fashionable thing discussed so often within classical circles now, brand identity. I was also curious to know what advantages perceives Gärtner within the in-house label paradigm – Bayerische Staatsoper certainly isn’t the first big organization to do it (the Berlin Philharmonic is another notable example) but the challenges of the recording industry (and the weight of being 500 years old) are no small thing. What role does (or should) an independent label play in a decidedly difficult classical landscape? How to choose archives? What about new work? Whither relevance (another word so frequently thrown around in the classical world)? And what’s with the BSOrec design? Gärtner has the answers, and then some.
Why have an in-house label?
People might look at the orchestra solely within the context of musical theatre, so for us, being in charge of our own musical well-being, and our own concert performances, is a very strong and vital thing. We don’t just play because it’s fun – that’s a big part – but we want to be seen, and we want people to know what we stand for and why we do what we do. The key is to be accessible and visible; we don’t always travel, but the media travels for us.
With the Mahler 7 release, it was a stunt to start – we are an opera label but we made our introduction with a big symphony. We showed the world that the Bayerisches Staatsorchester is not just an opera orchestra but one of the finest orchestras in the world. By doing that, and doing it successfully, we really made a point, and it worked out really well.
So for the Mahler CD and the Die Tote Stadt DVD we had two real gems, especially with Kirill Petrenko being one of the greatest of his art, and the orchestra under him being on top also. We knew that together there was something worth sharing and exploring. We always aim to show how much is happening in one house, so the recordings recognize the versatility of the orchestra but also the entire system in our house, and how deep and broad it all actually is. We knew from the beginning it wouldn’t be just operas, or just concerts we would release, but everything this house produces, which is why we decided to release ensemble work as well.
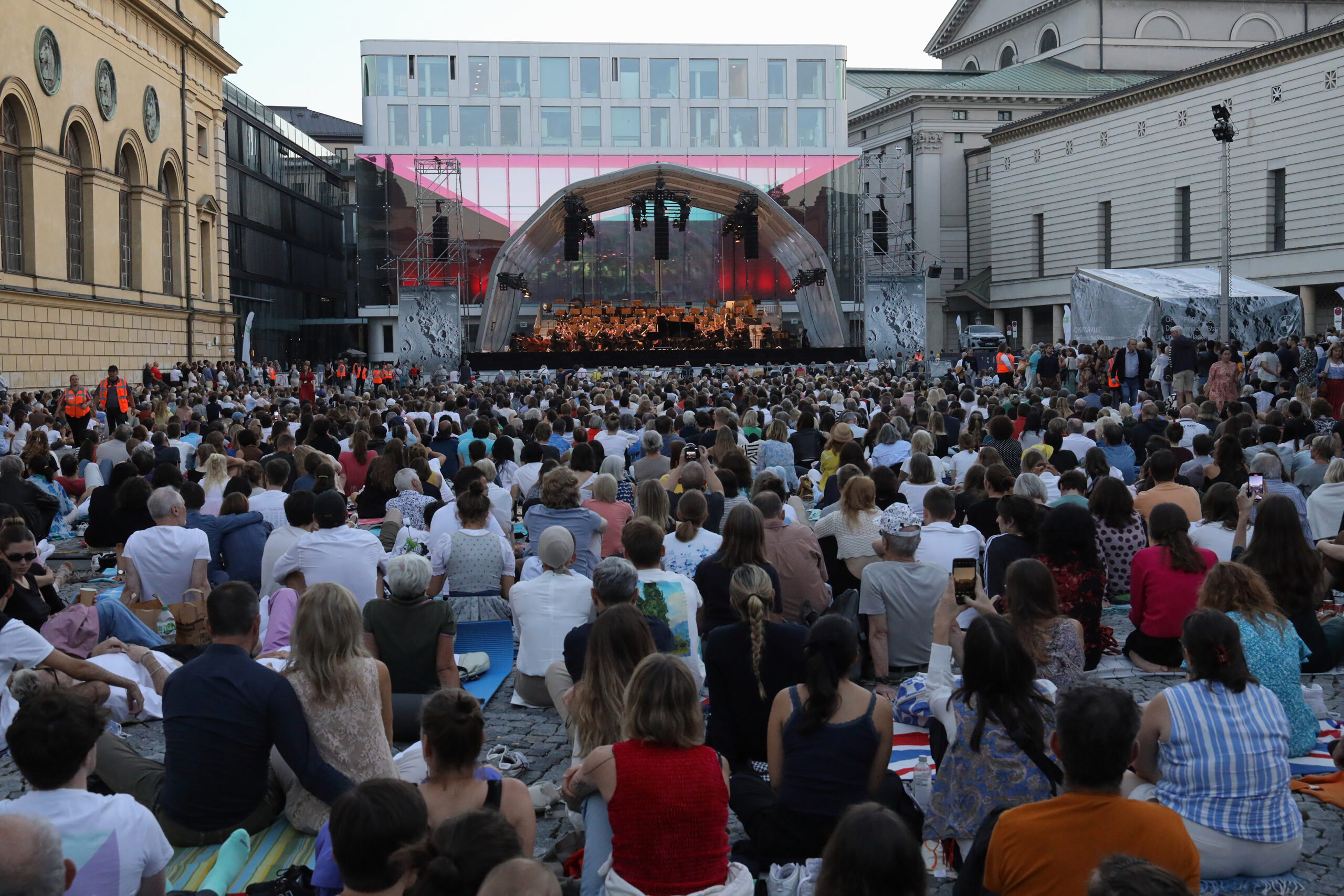

Bayerische Staatsoper’s Oper für Alle concert featuring Bayerisches Staatsorchester performing at Munich’s Marstallplatz, September 16, 2023. Photo: Wilfred Hösl
How does that label change or influence your position within the classical ecosystem of Munich?
It’s amazing – we have this relatively small city with this extremely large amount of fantastic musical institutions and ensembles like the Bavarian Radio Symphony Orchestra and the Munich Philharmonic. At the BSO we are always telling a story; I always say, it’s stopping the heart. A C# minor chord is never just a chord but a statement, part of a larger story. That goes for onstage work as much as recordings. What makes the orchestra so special is not that it’s the oldest one in Munich but it’s actually an orchestra whose DNA derives from theatre music: there’s spontaneity; there’s agility. But every orchestra stands for itself, and there’s enough space for all of them, especially in a city like Munich, which has so much music, and more widely in the state of Bavaria. We are very happy where we are. The Bayerisches Staatsorchester is identified as a theatre orchestra, as an opera orchestra, and we’re not trying to get away from that, but the point we’re making is we have even more to offer.
In terms of strategy and artistic development, it’s important to develop this awareness – if you want to survive as an orchestra I think it’s very important everyone knows why you exist. The education programs; the concerts and chamber concerts; the children’s pieces; things done within the community; the recordings: if you have all of these things to offer, it’s difficult to say you’re irrelevant. Relevance is everything to an orchestra.
Relevance seems very connected to BSOrec’s brand – what was the thinking behind its cultivation?
Being your own brand is powerful. Our in-house label gives us the freedom to choose which repertoire we want to release, because we genuinely like it. But more importantly, this choice gives us the possibility to influence how we are being perceived, not only as a label, but also as an artistic institution. As opposed to a major label, in our case the institution and the label are the same brand. That is an absolutely important element that gives us a lot of freedom.
How does this sense of freedom help to attract audiences, especially those new to the art form or those who know you exclusively for opera?
We can show what’s actually in the orchestra –who we are, what we do and where we come from. We can of course show what incredible musicians we have. There are so many different people with so many different interests and styles. There’s also the possibility for that thing I mentioned before, storytelling: we tell stories about Strauss’s father, who was a horn player; we tell stories about various aspects of contemporary music; we offer tales on new aspects to well-known music that has been here for a long time. The label offers a microscopic view into the orchestra. The first archived recording being released is also a very important block in the overall idea of the label and tells its own story.
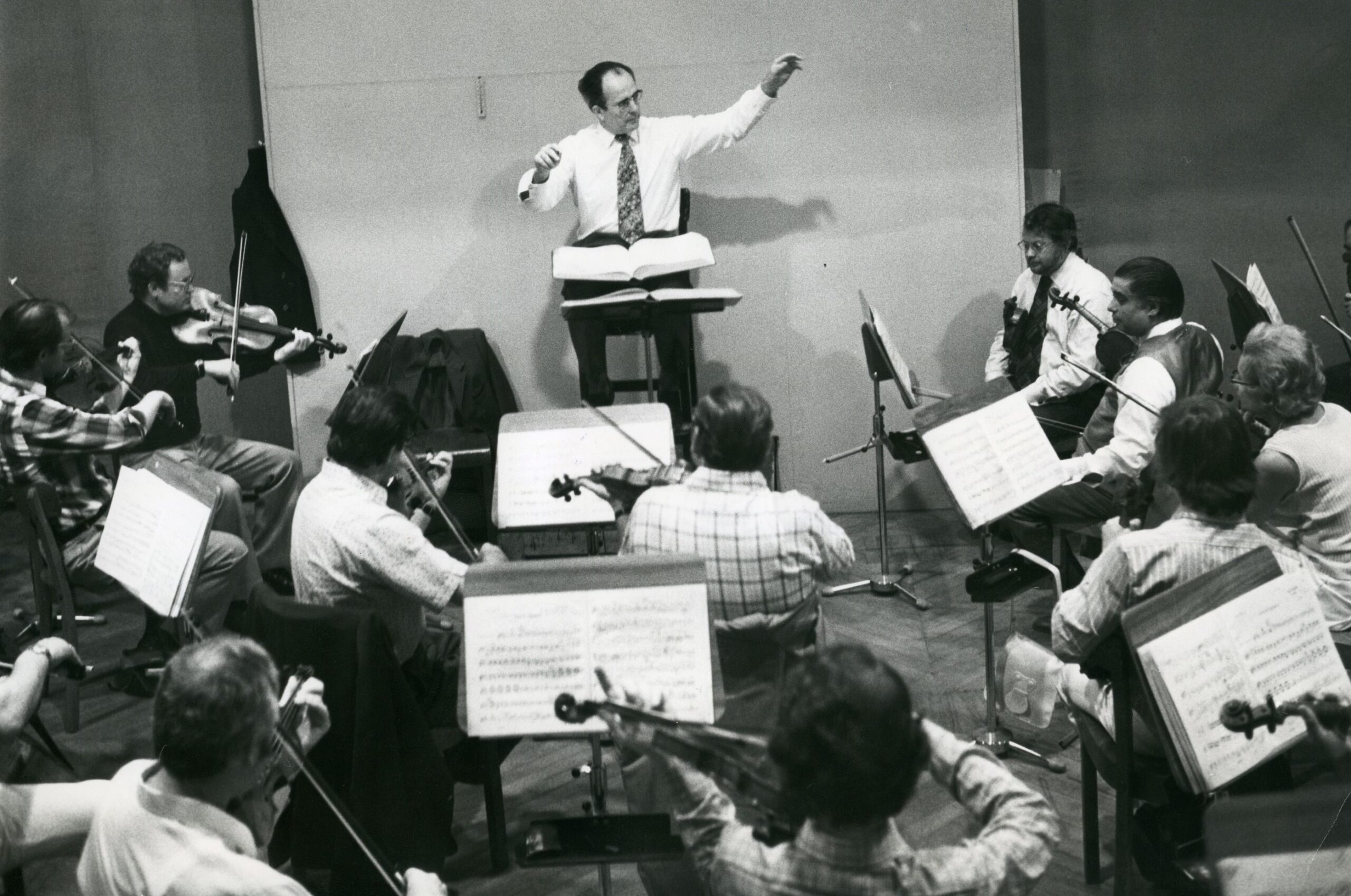

Wolfgang Sawallisch in rehearsal. Photo: Sabine Toepffer
How do you find new approaches for archived recordings?
It’s an interesting question. For this latest release, Mendelssohn’s Elias, the statement is: it isn’t an opera; it isn’t a symphonic work; it’s an oratorio. It shows the versatility of the orchestra but first and foremost it shows the excellence. The cast and the orchestra are a dream team. It’s not that they just convened for this one thing and took off to various places when it was finished; all of these singers were often guests in the National Theatre back in those days. It’s not just one moment in the history of the house but shows the general level that was here in 1984. Also, this piece was premiered for both the Münchner Opernfestspiele and the 88th German Katholikentag (Catholic Convention). It’s music composed by someone with a Jewish background who converted to Protestantism. Sawallisch was also making his own statement on unity and religious beliefs.
When I first listened to the recording, it didn’t take me long to realize this is something we have to publish, because it was a moment, because there was so much energy in the room, and you can really hear it. In so many ways it felt like the perfect way to start the archived releases for the label.

Conductor and Bayerische Staatsoper GMD Vladimir Jurowski speaks with composer Victoria Vita Poleva before Bayerisches Staatsorchester’s performance in Berlin, September 11, 2023. Photo: Wilfred Hösl
What is the role of new compositions then?
The idea was always to give contemporary music a real platform. We started with Mahler, yes, then released Die Tote Stadt; we knew those two would have momentum and be successful. They would give the label a good entrance into the world and get everyone interested in the next release. The next release after them was a contemporary opera, Hans Abrahamsen’s The Snow Queen, a project not many labels would have taken on. The other thing we released was Beethoven 2 – by the way that was the main piece played in 1811 at the inaugural Akademie concert – and that symphony was combined with a contemporary piece by Brett Dean. His “Testament” relates to the Beethoven immediately and also showcases Vladimir Jurowski’s approach to music and programming, which I find highly interesting.
For the Voyager release there was a contemporary work by Konstantia Gourzi, who wrote it specifically for the Munich Opera Horns. The entire album circles around her “Voyager 2”, which I find very strong, and which was chosen by the musicians themselves, as was the contents on the whole album. We didn’t intervene, because I like to think musicians have fantastic ideas when it comes to this kind of a project.
I like the idea of the Trojan Horse: as was seen with the Beethoven release, it’s good to combine the big great old repertoire with something brave and new, something that speaks to our time, and gets attention because of the combination. It’s an approach Jurowski uses a lot, and it works when you do it well. You have to find a good balance between everything and I’m sure the label will try to keep going in that direction.
To what extent does BSOrec’s package design reflect this balance?
When you see releases from other labels, you see the piece in big letters, or more often these days the singers, and in small letters you see the institution – the house isn’t the main thing. If you put those productions from all these labels in a row, everything looks different and what you recognize is the piece. But if you now put all the BSOrec releases together, it’s very clear which institution is behind it. It’s clear. The idea is, it isn’t about pictures, it’s about institution, and many different repertoire styles; it also signals a certain quality, and a certain idea or concept, all within one house. The door you open to all of that looks the same. I won’t tell you which colours are next – that’s the magic trick! But it’s always nice that people ask about that particular thing.
Interesting the DVD features Jonas Kaufmann and Marlis Petersen in what was a very acclaimed production but their photos aren’t on the cover – that’s a brave choice!
It equalizes. Some love it, some hate it. Whenever you see it it sticks out, and that of course is the oldest trick in the branding book: recognizing a logo or a certain style. And that style has to match the idea, and have the quality of the physical in terms of how the products feel when you touch them. All of this is important, but all of it, entirely, has to precisely match the musical content, the production content, but also, the written content. This is why I’m so grateful to have Malte on the team. The booklet, the music, the style, the sound, the way it feels in your hand – it all has to be one experience and it has to be a fine, subtle, and beautiful combination to give you one beautiful experience.
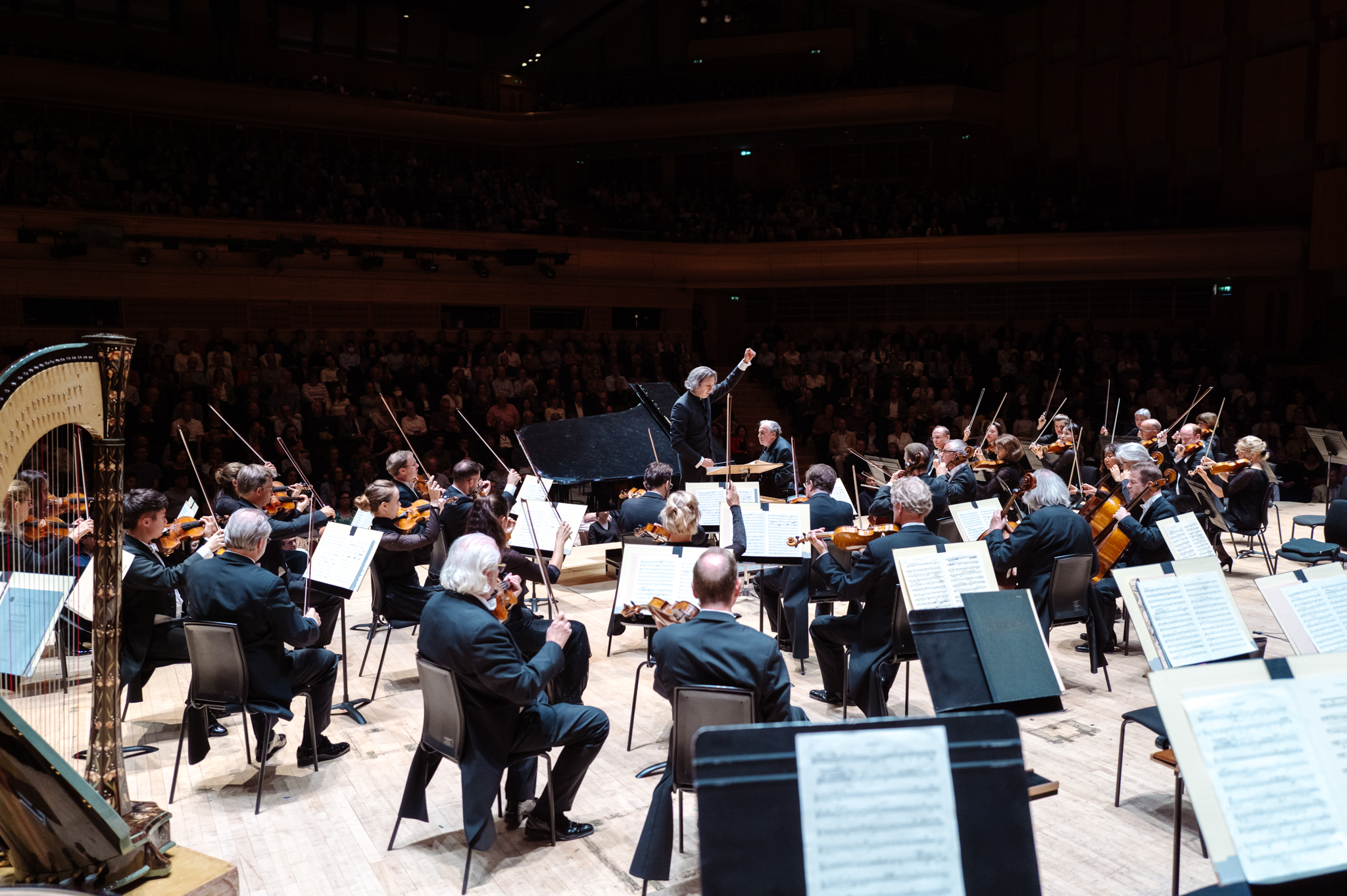

Bayerisches Staatsorchester performs under the baton of Bayerische Staatsoper GMD Vladimir Jurowski in London on September 19, 2023. Photo: Geoffroy Shied